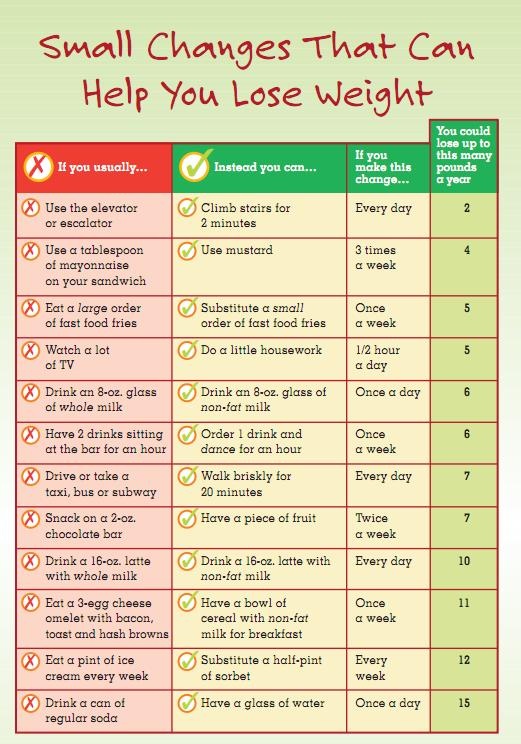
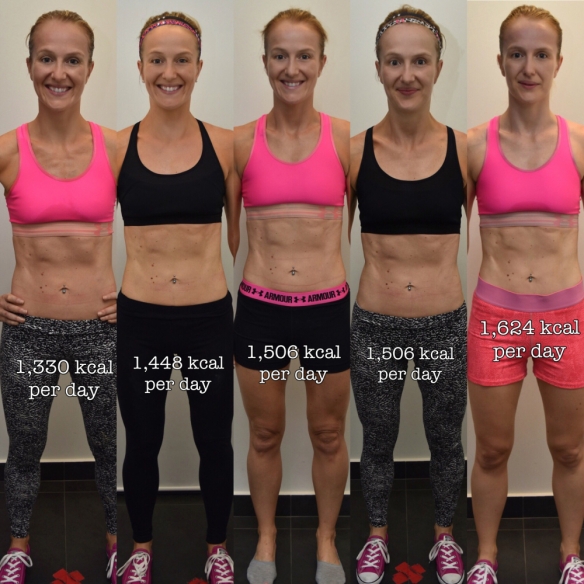These days, a lot more clients are interested in their lean gains rather than just their weight loss – and I love it. The number on the scale means nothing (and is, in fact, useless for my profession) since it cannot speak to the distribution of fat and muscle that actually determines optimal health.
So what does matter, then?
Body fat. Muscle mass. And the ratio between the two.
Perhaps you’ve heard of the “skinny-fat” phenomenon – whereby someone’s body weight puts them in the optimal Body Mass Index (BMI) category (since BMI is ONLY a measure of height to weight), but their body fat percentage puts them in the obese category (charts for each of these categories for men and women can be found here).

No, I didn’t just choose her because of her outstanding name. This particular woman did NOT lose weight – she simply transitioned from 32% body fat (LEFT) to 25% body fat (RIGHT) at the SAME weight, meaning she became “less fat” though not necessarily “skinnier.”
On the fat opposite side of the spectrum from skinny-fat is of course the bodybuilder physique, whereby the sheer density (weight) of one’s body would put them in the “obese” range for BMI, but their body fat levels are extraordinarily low (single-digits for men).

This woman is VERY petite and VERY muscular. Her body weight puts her at the edge of the “obese” BMI. Her physique, clearly, is not that.
Sure, there are plenty of philosophical and political problems with the “strong is the new skinny” movement, many of which have to do with the fact that comparing ANYTHING against “skinny” means that it still maintains some sort of elusive elite status (which it surely should not).
But I will maintain that for the majority of my clients, gaining lean mass, dropping excess body fat, and building strength through powerful movement (for example, learning how to do a clean and press correctly) is the best way to develop lasting fitness (and yes, lose weight, if that’s something you need to do for better health).
So how do we actually do those things?
The key to changing body composition (as with so many things related to our body and how it looks and feels) is DIET. There are certain foods that are FANTASTIC for building and maintaining lean mass, and others that are great for dropping fat and accelerating a fat-burning metabolism – so here’s a rundown of my favourites (besides chicken breast and broccoli, which I feel like are the basic-basics everyone knows):
- Eggs. The incredible edible. Perfect protein; healthy fat. Low cal. And versatile AF!
- Greek yogurt. If you can do dairy – this is the one. Protein packed. Creamy. Filling. Substitutes for sour cream, cream cheese, all sorts of things. Win!
- Tuna. Cheapest quality protein source in town (watch the mercury!). Portable with no refrigeration. Mixes with a lot of stuff (try spicy mustard or hummus).
- Shrimp. Super low-calorie protein that plays well with a lot of different dishes (soups, curries, even sandwiches when you chop it up and make a little salad)
- Avocado. Super high in fat, sure – but it’s the good kind, the kind that keeps you full and encourages your fat-burning metabolism
- Salmon. Omega-3 rich; tasty AF; high in protein; versatile in recipes; even better raw. Quadruple win.
- Nut butters. Make sure you choose the ones with JUST nuts as the sole ingredient, and watch the portion (up to 2TB daily for women; 3TB for men; 4TB for active gainers).
- Protein powder. A great option for vegetarians, picky eaters, or those always eating on the go, find a high-quality product with AT LEAST 40g protein for 200 or fewer calories and 0-3 grams of carbs. This is the one I recommend most.

On a related note, here’s some “I thought that was healthy!” stuff that you can definitely DROP from the diet when trying to gain lean mass and lose fat:
- Fruit/juice. Think of it as a slightly healthier soda. Pure sugar.
- Hummus. Nothing wrong with hummus in moderation, but let’s be real: hummus is a blend of carbs and fat, and it’s often eaten with more carbs (crackers, carrots) and in more of a portion size than I’d recommend to most of my fat-loss clients.
- “Whole grain” processed food. Again, slightly healthier flour/sugar bombs.
- ANY OTHER yogurt besides the above. Sugar bomb without the protein to back it up. Catch a theme here?
- Oatmeal/granola. Mostly those little pre-sweetened packets of the former (plain oats do have some great health benefits, though the portion size is so small for the calorie/carb dent), and almost every variety of the latter.
- Bars/balls/squares/whatever-the-hell-shape of calorie & sugar-dense junk. Outside of QUEST or Rx Bars (which I still only recommend as a backup plan to actual food and meals), most of these things are shockingly high in calories, carbs, sugars, and saturated fats. If there’s no label, that doesn’t make ’em healthier – and can often hide the high calorie density of things like dates, coconut oil, and nuts.

Beware these little buggers. The ones featured here have over 200 kCal apiece!
- Nut butters. But wait – weren’t these just on the LOSE fat list? Yes, my friends – but for some dieters, the allure of the PB is too much to bear – and the 2TB portion (which is still calorie-dense as a single serving) slips into 4-5TB without even realising it – and suddenly you’ve eaten the equivalent of a half pint of Ben & Jerry’s (!).
Again, folks – calorie math is still at the baseline of the equation of weight loss: if you eat more calories than you burn, you will not lose weight. But the composition of those calories – the ratio of macronutrients (protein/carbs/fat) and quality of the foods from which you get those nutrients – is crucial to how you look, feel, and perform.
For optimal fat loss and muscle gain, I recommend a steady diet of lean proteins alongside ample servings of vegetables and healthy fats, with beans/grains/fruit in moderation for fibre and fullness. Exercise-wise, add mostly resistance training (ideally with weights, ideally under the coaching of a professional) alongside moderate cardio (ideally walking, ideally at least 12K steps daily) for heart health – and you’ve got my best advice.
What do you eat to feel healthy? What foods make you feel vibrant and alive?