Last weekend my partner, friend and I conquered the Spartan Beast Malaysia. For those of you unfamiliar, here’s a quick summary:
- 21K (13.1 mile) outdoor trail course including hills as steep as 16-20% grade; 25-30 obstacles with a 30-burpee penalty for noncompletion; water crossings and mud as deep as your knees

Pro marathon tips.
Just six days prior to that, my partner and I also completed the Standard Chartered Singapore Marathon, and while I know you all understand what a marathon (42K / 26.2 mile) means, the SCSM also means:
- a death-march, double-back and out-and-back-filled course starting in the pitch black of night at 4:30am and performed in 90-95% humidity from start to finish
To put it mildly, I’m good on endurance events for a while. Maybe forever.
I’ve done a lot of reading about the impact of endurance training and racing not only on an athlete’s body, but on a woman’s body in particular (granted, I’m not exactly built like a typical woman either what with my giant shoulders and long arms, but whatever).

There was a time when I solved the problem of “too much running” by training for triathlons (swim-bike-run combo events) and making sure I balanced the pounding on my joints with some good old-fashioned flotation and cycling therapy. But to be honest, with my current schedule and commitments, triathlon training just isn’t viable time-wise or expense-wise (those carbon-frame bikes don’t come for free, yo).
But these days, I vacillate between feeling completely unmotivated to get out and run 20 or 30K every weekend (ugh) and feeling completely destroyed after I inevitably do because I know I need to do it for training (double ugh).
Couple this with the fact that my partner nearly died twice on the aforementioned events (ok, death obviously averted, but he suffered from crippling calf cramps in both races and some nagging injuries afterward) and both of us are a bit burned out on the whole idea of slogging long distances for the sake of pride.
So what’s next?
I’ve signed up for the Zoo Run 10K just to see if I’ve got my speed chops still kickin’ (most recent PR was last year’s 3rd-overall finish of 43:28. which I fear I will never again beat) and I want to try a 5K in February or March for the same reason.
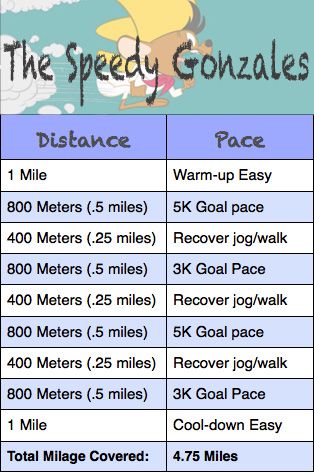
Looking at “meters” rather than “kilometers” gives me LIFE
I also want to set goals that aren’t just related to speed/racing/running, such as getting back into yoga (I was doing it at least 1X/week for so long, and in 2017 I only did it twice in the entire calendar year), getting stronger at Olympic and basic lifts (definitely going to keep up my Orangetheory and Garage habits), rediscovering my weekly stairs workout and boxing routine, and working on shortening and intensifying my workouts in general.
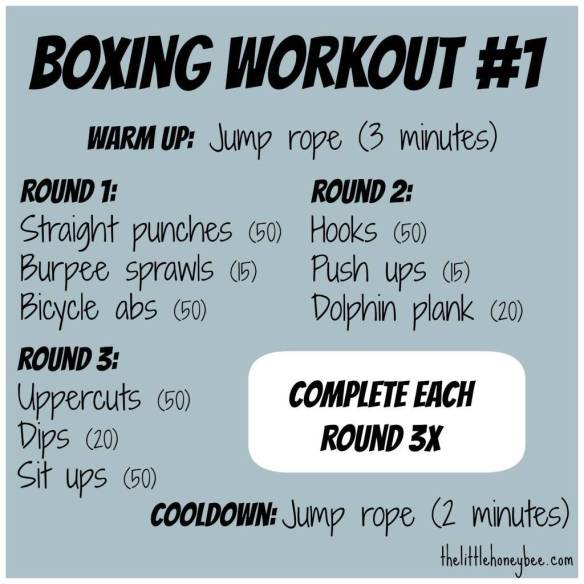
Short and not-so-sweet; that’s why I LOVE boxing
I want to get back to the track and feel truly fast again. I want to remember what it feels like to inspire a group of people by teaching energetic group exercise (namely Spin). I want to punch something (to refrain from punching someone, haha). I want to just be free to move my body in ways that aren’t designated by a training plan or competition.
This ol’ bod is telling me it’s time for a change – and as they say in my line of work, if you listen to your body when it whispers, you’ll never have to hear it scream.
How are you going to spruce up your workout routine in 2018?